Table of Contents
1. What is a BLDC Motor?
A BLDC motor (brushless DC motor) is a motor with high efficiency, high torque, and a long lifespan.
It is widely used in home appliances, industrial equipment, and automotive components due to it's low noise factor and power saving ability achieved through high efficiency.
The BLDC motor is broadly categorized into two types of structures: a single-phase BLDC motor which is widely used in small fan motors, and a three-phase BLDC motor which is widely used in air conditioners and power tools.
Here we introduce the structure and drive system of the three-phase BLDC motor, which is currently the gold standard in the market.
2. Three-phase BLDC Motor
A three-phase BLDC motor consists of a rotor, which contains a rotating permanent magnet, and a stator, which contains a coil, that generates the magnetic force to rotate the rotor.
An inner rotor BLDC motor is one in which the stator is fixed on the outside, and the rotor rotates on the inside. An external rotor BLDC motor is one in which the stator is fixed on the inside, and the rotor rotates on the outside.
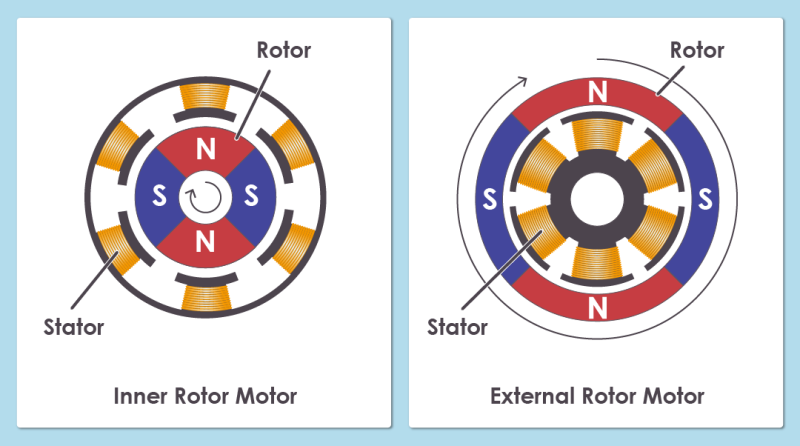
The inner rotor BLDC motor can be configured in compact size. It features high controllability due to its small moment of inertia.
In comparison, the external rotor BLDC motor has a high degree of freedom due to its magnet size and a coil structure, similar to that of a conventional brushed DC motor, therefore it is easy to manufacture.
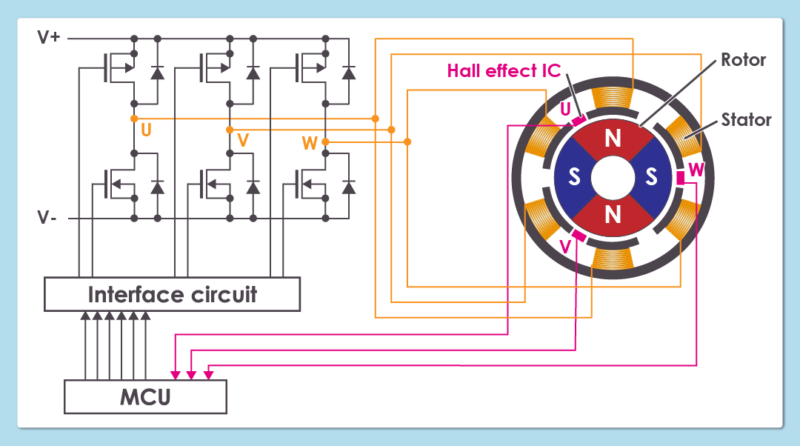
3. Role of the Position Sensor (Hall Element and Hall Effect IC)
Position sensors used in a BLDC motor can be divided into two main types: (Type 1) sensors that detect the absolute angle of the rotor, and (Type 2) sensors that detect the rotational position of the rotor.
An absolute angle sensor such as an encoder, or a resolver is used for (Type 1), while a rotational position sensor such as a Hall element or a Hall effect IC (also called a Hall sensor), is used for (Type 2).
The Hall element and Hall effect IC used in BLDC motors are utilized as a position sensor to detect the rotational position of the rotor.
Since the BLDC motor switches ON and OFF the current flowing to the stator coil by detecting the rotor's rotating position, the positional relationship between the stator and Hall element or Hall effect IC is entirely important.
Therefore, there is important acquired knowledge needed when creating a board to mount the sensors.
Hall Element
A Hall element outputs a potential difference corresponding to the magnetic flux density received.
Because an analog voltage corresponding to the rotational position is obtained, it is possible to set an arbitrary threshold value in an MCU or a controller, and to implement analog control according to the voltage.
It is important to note that the MCU or controller needs to receive the analog voltage from the Hall element, so a high-speed AD converter, amplifier, and comparator are required. Generally, MCUs and controllers are designed exclusively for BLDC motor control and thus have optimized comparator circuits.
In addition, signals outputted from the Hall element have high impedance and are easily affected by electromagnetic noise generated around the stator coil and motor, so sufficient noise countermeasures must be implemented to prevent malfunctions.
Hall Effect IC
A Hall effect IC integrates a Hall element and signal processing circuit such as an amplifier. A bipolar Hall effect latch IC and the ZCL Hall effect IC used in BLDC motors output low impedance logic signals. The Hall effect IC is extensively used in motor environments with high noise levels.
MCUs and controllers can be configured with simple functions and at a low cost, since the digital signals from the Hall effect IC are input to them, it eliminates the need for an AD converter, amplifier, and comparator.
For a technical description of the Hall element and Hall effect IC, please refer to "What is Hall effect IC?"